 eEQP-2025: eEQP-JapanTRIZSympo-2025 eEQP-2025: eEQP-JapanTRIZSympo-2025 |
|
Earthquake Prediction Research Based on the TRIZ Philosophy (2)
R&D with a Clear Vision of the Goal of Real Application |
Toru Nakagawa (Emeritus Professor, Osaka Gakuin University)
Presented at TRIZ Symposium 2025 � (Held by Japan TRIZ Society,
on Sept. 4-5, 2025, at Waseda University, Tokyo)
|
Posted here: Sept. 14, 2025; Japanese page: Sept. 14, 2025 
|
Posted: Sept. 14, 2025 |
For going to Japanese pages, press  buttons.
buttons.
Editor's Note (Toru Nakagawa, Sept. 14, 2025)
I gave this presentation on September 5 at the 21st Japan TRIZ Symposium. The subject of earthquake prediction is excptional in the TRIZ community, although it is of interest to them just as general public in Japan. So I tried to present the paper as clearly and broadly as possible toward a general audience, not specialized in seismology or earthquake forecasting/prediction.
The contents are based (and further developed) on my paper presented last December at the Earthquake Prediction Society of Japan (EPSJ) Conference.
The key points, particularly based on the TRIZ philosophy, are as follows: the vision of the final stage of social application of earthquake prediction research is presented, even at the current early stage of research. Criteria are clearly defined for the requirements for effective earthquake prediction methods, and are applied to focus on several promising methods. Stages of developing and verifying the technological system of prediction methods are proposed.
I post the following documents in this website:
|
Japanes page  |
English page  |
Abstract |
Abstract (.html)  |
Abstract (.html)  |
Presentaation slides |
Slides (18 slides)  , ,
(.pdf, 4 slides/page) |
Slides (18 slides)  , ,
(.pdf, 4 slides/page) |
Presentation video |
Video (.mp4, 23m45s, 500 MB) |
|
 Abstract
Abstract
Research Based on the TRIZ Philosophy (2)
Research and Development with a Clear Vision of the Goal of Real Application
Toru Nakagawa (Professor Emeritus, Osaka Gakuin University)
Presented at Japan TRIZ Symposium 2025 on Sept. 5, 2025
Abstract (Submitted on May 19, 2025)
Because the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake (1995) and the Great East Japan Earthquake (2011) were never foreseen nor predicted, the Seismological Society of Japan (SSJ) and the Government have declared that "Earthquake Prediction is impossible with current technology." And they decided not to work on EQ Prediction but rather on observation of EQs, basic research into the EQ mechanisms, and EQ disaster mitigation measures. The most public in Japan, on the other hand, still has a strong desire to make the EQs predictable for reducing the damage on human and society significantly.
Research into EQ Prediction, has remained, until recently, in a state of groping in the dark in the World. Fortunately, we have seen some clear clues since 2 – 3 years ago in Japan.
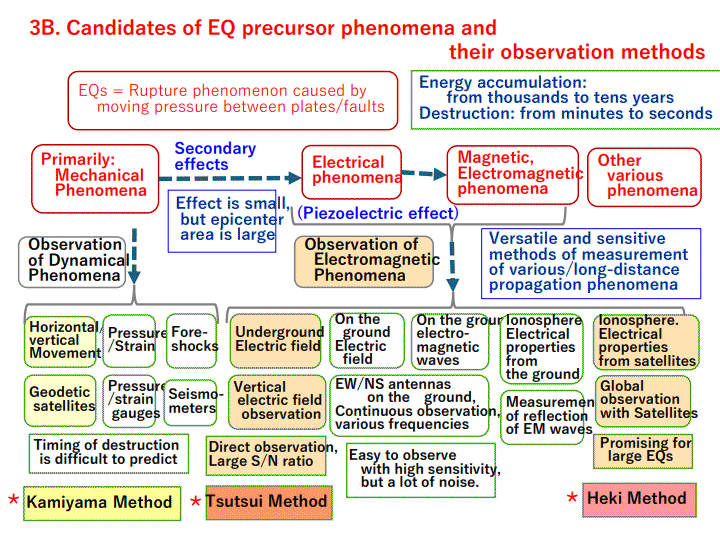
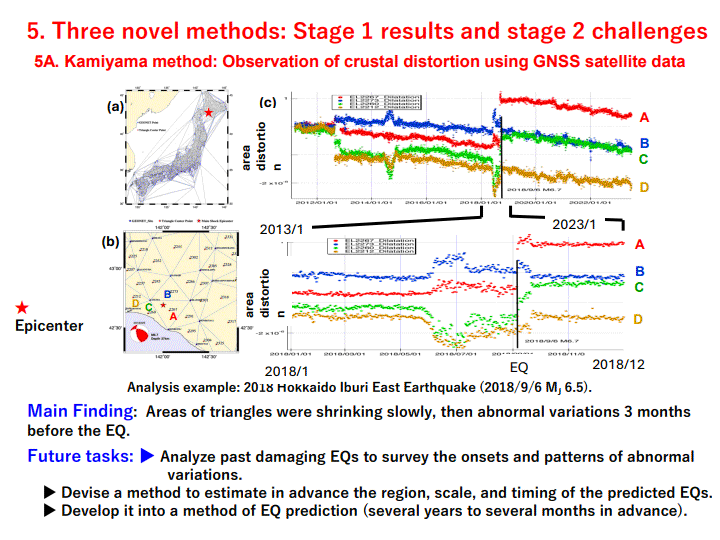
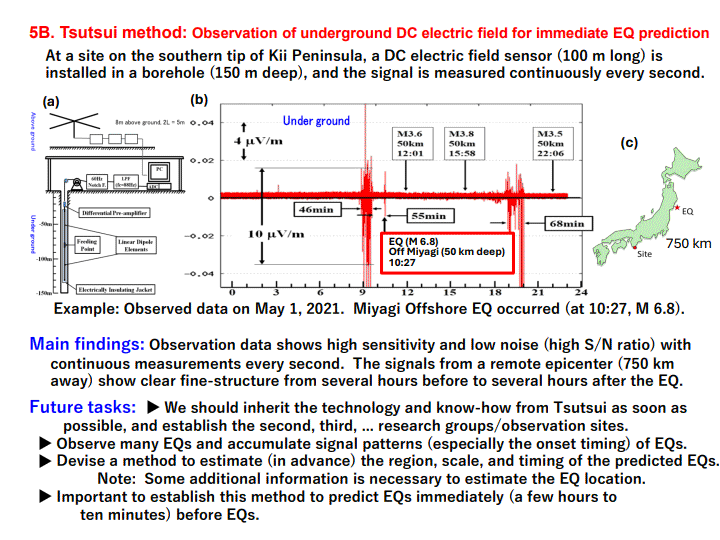
The first clue is Kamiyama method, which analyzes the GEONET data of crustal movement to detect abnormal variation a few years to a few months before EQs. The second clue is Tsutsui method, which observes the DC electric fields deep underground continuously to detect drastic fluctuations of signals from a few hours before to a few hours after EQs.
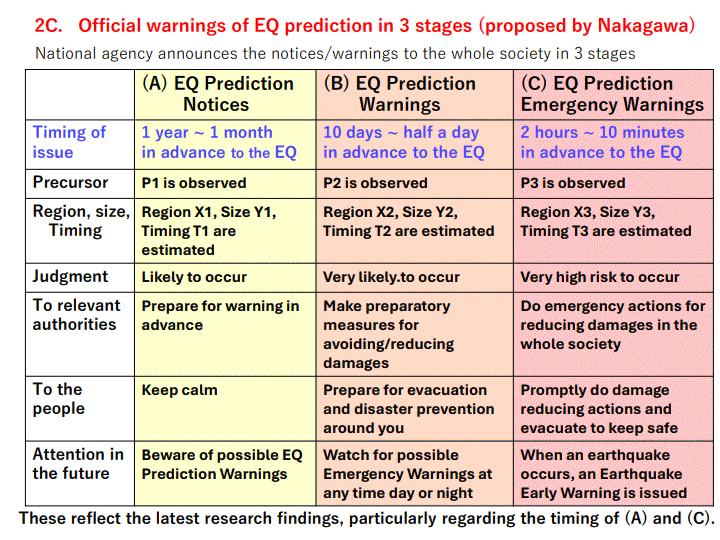
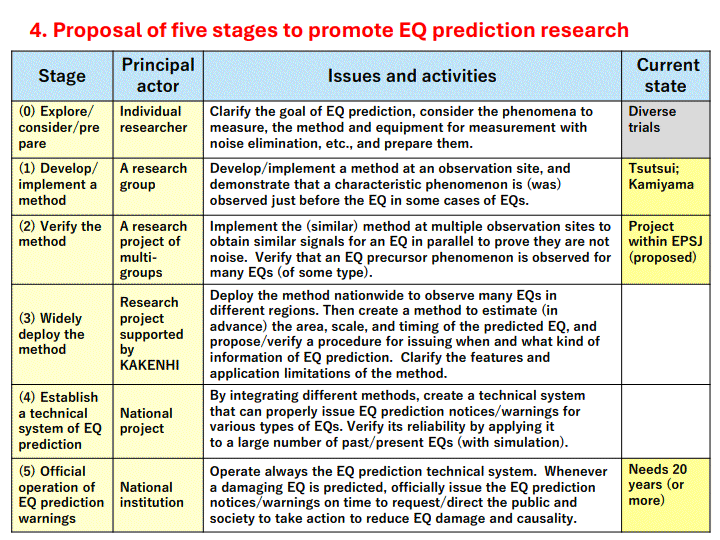
The vison of the final goal ("The Ideal Solution" in TRIZ) is shown in the following Table. Three stages of EQ Prediction Warnings are to be issued officially by a national agency before significant EQs.
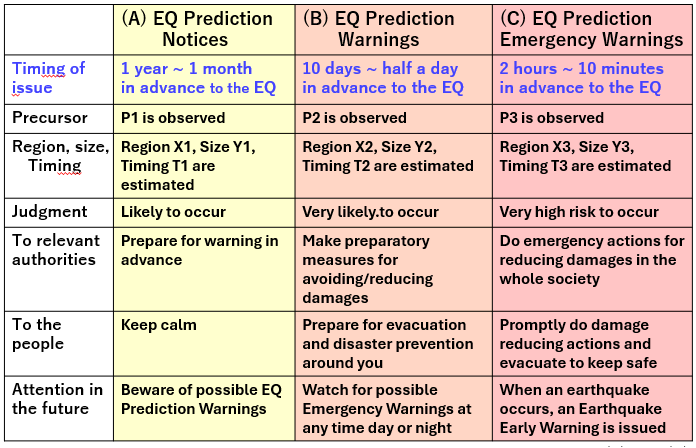
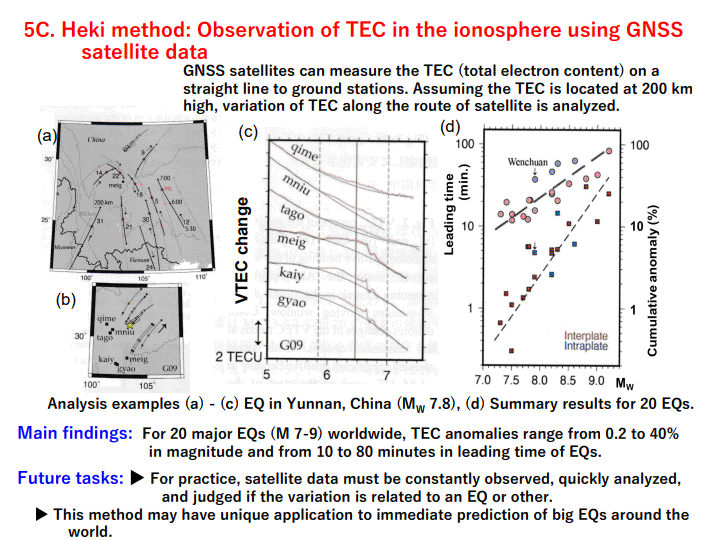
Kamiyama method may be used to issue (A) EQ Prediction Notices. Its current weak points are being less sensitive for the EQs occurring in the ocean or deep underground on land, and still not clear yet to predict the timing of EQ at the stage of close to its occurrence. Tsutsui method is promising for (C) EQ Prediction Emergency Warning. It can detect precursor signals a few hours to half an hour in advance and with high sensitivity for far-away EQs on land or under ocean. It has to overcome the high cost of setting the instrument deep under the ground at some remote (less noise) site. For estimating the EQ location, this method may need some additional type of observation data. Methods by Heki and by Umeno, both using the observation of electrical anomaly in ionosphere with satellites, may support issuing the (C) Emergency Warning.
Nevertheless, no clues have been found yet of the methods to issue (B) EQ Prediction Warnings. The Warnings, to be issued 10 days to half a day in advance, are expected to be most useful for people and society to prepare for disaster prevention and evacuation.
For realizing the EQ Prediction Warnings (A)(B)(C), we need intensive and large scale R&D of technological systems. I am proposing the Earthquake Prediction Society of Japan (EPSJ) to establish a Research Foundation to operate the collaborative research project. We will devote to make much and long -term efforts to gain the understanding by the Seismological Society (SSJ), academia, the media, the government, and the whole society, to make the EQ Prediction finally possible and useful for reducing EQ disasters .
 Presentation Slides ==> PDF (4 slides/page)
Presentation Slides ==> PDF (4 slides/page) 
Research Based on the TRIZ Philosophy (2)
Research and Development with a Clear Vision of the Goal of Real Application
Table of Slide Contents:
Title: Table of contents (brief) ... 1
1. Introduction: Background and Purpose ... 2, 3
2. Our ultimate goal: Disaster mitigation through the� public operation of EQ prediction notices/warnings ... 4
2A. Public issuance of EQ prediction warnings: division of roles
2B. Basic guidelines for public announcements of EQ predictions ... 5
2C. Official warnings of EQ prediction in 3 stages (proposed by Nakagawa) ... 6
2D. Template for the announcement of an EQ Prediction Notice (A) (draft) ... 7
2E Systems and preparations necessary for the official issuance of EQ prediction
... 8
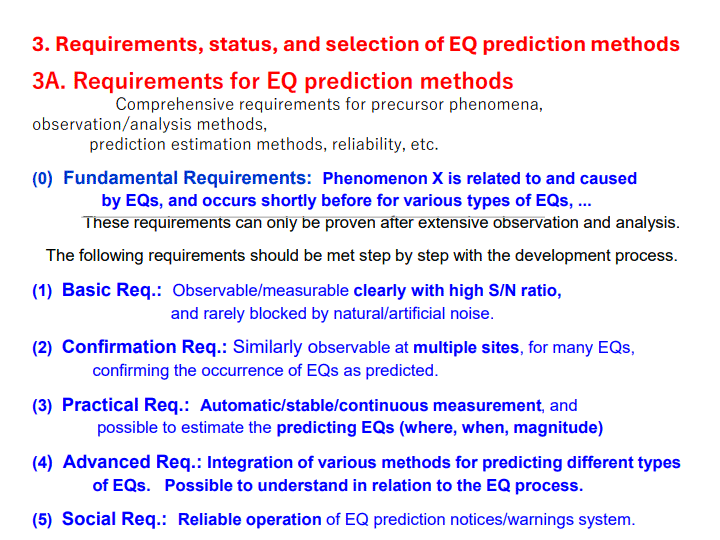
3. Requirements, status, and selection of EQ prediction methods ... 9
3A. Requirements for EQ prediction methods
3B. Candidates of EQ precursor phenomena and � their observation methods ... 10
3C. Evaluation overview of various methods (prospects) (Nakagawa) ... 11
4. Proposal of five stages to promote EQ prediction research ... 12
5. Three novel methods: Stage 1 results and stage 2 challenges ... 13
5A. Kamiyama method: Observation of crustal distortion using GNSS satellite data
5B. Tsutsui method: Observation of underground DC electric field for immediate EQ prediction ... 14
5C. Heki method: Observation of TEC in the ionosphere using GNSS� satellite data ... 15
6. Current challenges in EQ prediction research ... 16, 17
7. Summary ... 18

1. Introduction: Background and Purpose

2. Our ultimate goal: Disaster mitigation through the� public operation of EQ prediction notices/warning




3. Requirements, status, and selection of EQ prediction methods
4. Proposal of five stages to promote EQ prediction research
5. Three novel methods: Stage 1 results and stage 2 challenges
6. Current challenges in EQ prediction research


7. Summary

Last updated on Sept. 14, 2025 Access point: Editor: nakagawa@ogu.ac.jp


















