For going back to Japanese pages, press  buttons.
buttons.
Editor's Note (Toru Nakagawa, Mar. 1, 2016)
I gave this Keynote Lecture at ICSI 2015 (6th International Conference of Systematic Innovation) in July last year at Hong Kong. At the conference, I gave the Tutorial Lecture on USIT on the first day for 3 hours, and then this Keynote Lecture on the second day morning for 60 minutes. Thus assuming that many of the audience attended at the USIT Tutorial, I talked here on the more important concepts of the 'Six-Box Scheme', which was derived from USIT and forms the new paradigm of 'General Methodology of Creative Problem Solving' (CrePS). The Keynote reflects my research history for these 18 years since I first met TRIZ in 1997.
The lecture has 47 pages of slides, as posted here in PDF. The outline of the slides are shown below, and also in the Japanese page.
Hints (TN, Feb. 29, 2016): In the PDF file  , each chapter head is book marked (thus you can jump to the page directly inside PDF) and is also destinated (thus you can jump into the page directly from the present Web page by clicking the
, each chapter head is book marked (thus you can jump to the page directly inside PDF) and is also destinated (thus you can jump into the page directly from the present Web page by clicking the  button shown in the following outline.)
button shown in the following outline.)
 PDF file of the Keynote Lecture:
PDF file of the Keynote Lecture:
Keynote Lecture: Six-Box Scheme: New Paradigm for Creative Problem Solving
==> PDF file  (906 KB, 47 pages)
(906 KB, 47 pages)
 Outline of the Keynote Lecture
Outline of the Keynote Lecture
Keynote Lecture: Six-Box Scheme: New Paradigm for Creative Problem Solving 
Title
Introduction 
Outline: 4 Stages of Recent Development of
Methodologies of Creative Problem Solving
Current status of research on CrePS/TRIZ/USIT:
'General Methodology for Creative Problem-Solving/Task-Achieving' (CrePS)
Methodologies of Creative Problem Solving:
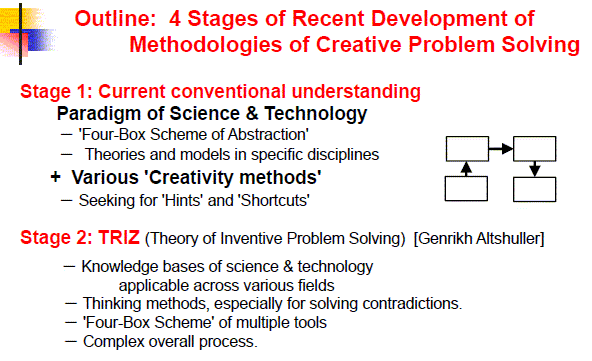
Stage 1:
Current conventional understanding: Paradigm in science and technology +
Various 'Creativity methods' 
Conventional Paradigm in Science & Technology for Creative Problem Solving = Four-Box Scheme of abstraction
For (discoveries and) inventions, (it is often assumed that) idea generation and enlightenments are important.
Many different approaches have been advocated
Various methods for creative problem solving & task achieving (Categorized with their approaches)
Isn't there any methodology more scientific and sure?
Stage 2:
TRIZ
(Theory of Inventive Problem Solving) [Genrikh S. Altshuller (ex-USSR)] 
Recently, 'Methodology for Creative Problem Solving' has been developed on the basis of TRIZ and its extensions.
TRIZ makes full use of knowledge in science and technology
Tools of TRIZ (Based on the Four-Box Scheme)
Overall Procedure in TRIZ (Darrell Mann's "HOSI" (2002))
Essence of TRIZ in 50 Words (Toru Nakagawa (2001))
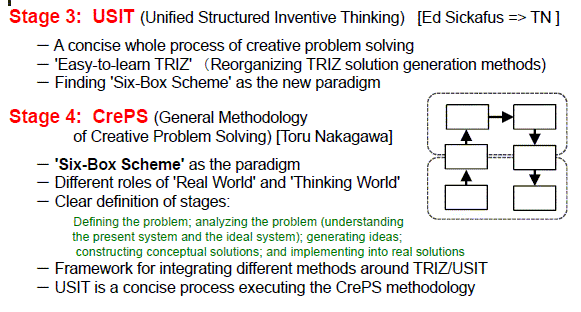
Stage 3:
USIT (Unified Structured Inventive Thinking) [Ed Sickafus (USA) ==> Toru Nakagawa (Japan)] 
USIT (Unified Structured Inventive Thinking) [Ed Sickafus]
USIT Procedure (Flowchart)
A Simple Case Study of USIT: How to fix a string shorter than the needle at the end of sewing
Define the Problem:
Problem Analysis (A): Understanding the present system
Problem Analysis (B) : Understanding the Ideal system
Solution Generation: Generate Ideas and Construct Solutions
"USIT Operators": A system of solution generation methods
-- Obtained by re-organizing all the solution methods in TRIZ
USIT Operators (A hierarchical system of 5 Operators and 32 sub-operators)
An example of USIT Operator sub-method: (1c) Divide the Object (into 1/2, 1/3, ..., 1/∞).
Examples of Application of USIT Operators:
An Example of USIT Operators (4) Solution Combination Method
A solution can be interpreted (or derived) in multiple ways
USIT Operators: Operator (5): Solution Generalization Method
Case study represented in the Six-Box Scheme:
How to fix the string shorter than the needle
New Paradigm of Creative Problem Solving:
(Six-Box Scheme of USIT) ==> (Six-Box Scheme of CrePS)
'Six-Box Scheme' (the Paradigm of CrePS)
Stage 4: CrePS (General Methodology of Creative Problem Solving) [Toru Nakagawa] 
Expected Areas of Applying TRIZ (We put TRIZ in the center. But we need a more general method !)
Reflection of the present situations around us and TRIZ
A new target at a higher level:
Target of Our New Methodology CrePS: "A General Methodology for Creative Problem Solving & Task Achieving"
The current status of research on CrePS/TRIZ/USIT: On-going research activities for developing CrePS
To relate CrePS to various activities in the 'Real world': Position of CrePS and its Six-Box Scheme
For Study and Practice 
For Mastering TRIZ/USIT: 2-Day USIT
Training Seminar
Practices of Introducing TRIZ/USIT
Implications of the New Scheme (3) Ideal expert
References: "TRIZ Home Page in Japan" --- Public Web site since Nov. 1998
Thank you
for your attention
Last updated
on Mar. 3, 2016 Access point: Editor: nakagawa@ogu.ac.jp

